Impacts of hinduism 1200 to 1450 – Unveiling the profound impacts of Hinduism from 1200 to 1450, this discourse delves into the multifaceted ways in which this ancient religion shaped the political, social, economic, cultural, religious, and artistic landscape of the era.
During this pivotal period, Hinduism played a central role in the formation of kingdoms and empires, shaping social hierarchies and caste systems, and influencing political and social life through its religious beliefs and practices.
Impacts of Hinduism from 1200 to 1450

During the period from 1200 to 1450, Hinduism played a pivotal role in shaping the political, social, economic, and cultural landscape of India. This era witnessed the emergence of powerful kingdoms and empires, the development of complex social hierarchies, and the flourishing of art, architecture, and literature inspired by Hindu religious beliefs.
Political and Social Impacts
Hinduism had a profound influence on the formation of political structures during this period. The concept of divine kingship, where the ruler was seen as an embodiment of the deity, was prevalent in many kingdoms. This divine mandate provided the ruling class with legitimacy and authority, and reinforced the social order.
Hinduism also played a significant role in shaping social hierarchies. The caste system, which divides society into hereditary social groups, became more rigid during this period. The caste system determined an individual’s occupation, social status, and access to resources.
Hindu religious beliefs and practices had a direct impact on political and social life. The concept of dharma, or righteous duty, guided the conduct of both rulers and subjects. Religious rituals and festivals played an important role in maintaining social order and cohesion.
Economic and Cultural Impacts
Hinduism influenced economic activities and trade practices during this period. The concept of varna, or social class, determined the occupations that individuals could pursue. Agriculture was the primary economic activity, and the cultivation of crops such as rice, wheat, and cotton was central to the economy.
Hinduism also had a significant impact on the development of art, architecture, and literature. The construction of temples, sculptures, and paintings flourished during this period, inspired by Hindu religious themes. The Ramayana and Mahabharata, two of the most important Hindu epics, were composed during this time.
Hinduism played a role in the development of education, philosophy, and scientific advancements. Monasteries and temples became centers of learning, where scholars studied religious texts, philosophy, and astronomy. The concept of reincarnation and the belief in a cycle of birth and rebirth influenced Hindu thought and philosophy.
Religious and Philosophical Developments, Impacts of hinduism 1200 to 1450
The period from 1200 to 1450 witnessed significant developments in Hindu religious beliefs and practices. The emergence of new sects, such as the Vaishnavas and Shaivas, led to a diversification of Hindu religious thought. Devotional movements, which emphasized personal devotion to a particular deity, gained popularity.
Reformist ideas also emerged during this period. The Bhakti movement, led by saints like Ramananda and Kabir, emphasized the importance of devotion and equality for all. The Advaita Vedanta philosophy, propounded by Adi Shankara, stressed the unity of the individual soul with the divine.
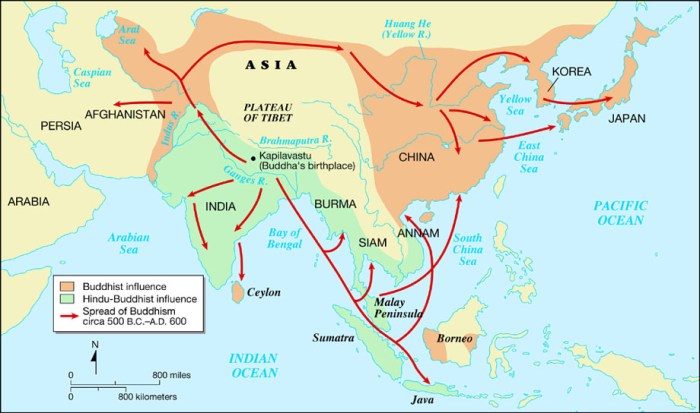
Hinduism also had a significant influence on other religious traditions and philosophies in the region. Buddhism and Jainism, which had emerged earlier, continued to flourish alongside Hinduism. Hindu ideas and practices were also incorporated into the development of Sikhism.
Literary and Artistic Expressions
The period from 1200 to 1450 witnessed the production of a rich body of literary works inspired by Hindu religious beliefs and themes. The Ramayana and Mahabharata, composed in Sanskrit, were widely read and performed. Vernacular languages also flourished, and poets such as Kabir and Mirabai composed devotional songs that expressed their love for God.
Hinduism had a profound impact on the development of art forms such as sculpture, painting, and architecture. Temples were adorned with intricate carvings depicting Hindu deities and mythological scenes. Paintings and sculptures were also used to illustrate religious texts and convey spiritual messages.
The symbolism and iconography used in Hindu art and literature were rich and complex. Animals, plants, and geometric patterns were often used to represent divine concepts and ideas.
Helpful Answers: Impacts Of Hinduism 1200 To 1450
What were the major political impacts of Hinduism during this period?
Hinduism played a significant role in the formation of kingdoms and empires, providing ideological and ritual support for rulers and shaping political structures.
How did Hinduism influence social hierarchies and caste systems?
Hinduism reinforced the existing caste system, with social status and roles being determined by one’s caste affiliation.
What were the economic activities and trade practices influenced by Hinduism?
Hinduism influenced economic activities such as agriculture, trade, and crafts, with religious beliefs and practices shaping economic practices and the distribution of wealth.