Spread of citrus in the mediterranean ap world history – The spread of citrus fruits throughout the Mediterranean region has been a significant historical and economic event, shaping the region’s agriculture, trade, and culture. This article examines the origins, dissemination, and impact of citrus cultivation in the Mediterranean, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating topic.
Citrus fruits, including oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, originated in Southeast Asia and were introduced to the Mediterranean region through trade routes and conquests. Over time, citrus cultivation spread throughout the Mediterranean, becoming an integral part of the region’s agricultural landscape and economy.
Origins of Citrus in the Mediterranean
Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, are believed to have originated in Southeast Asia, particularly in the region now known as India and Myanmar. From there, they spread to the Middle East and eventually reached the Mediterranean region through various routes.
Possible Routes and Methods of Citrus Introduction
- Trade: Merchants from the Middle East and North Africa likely played a significant role in introducing citrus fruits to the Mediterranean. They established trade routes that connected the East with the West, facilitating the exchange of goods, including citrus.
- Conquest: The expansion of empires, such as the Roman Empire, contributed to the spread of citrus. As Roman legions conquered new territories, they brought with them various agricultural practices, including the cultivation of citrus fruits.
- Pilgrimage: Religious pilgrims traveling to the Holy Land may have also played a role in introducing citrus to the Mediterranean. They could have carried seeds or saplings back to their homelands, contributing to the spread of citrus cultivation.
Spread of Citrus through Trade and Conquest: Spread Of Citrus In The Mediterranean Ap World History
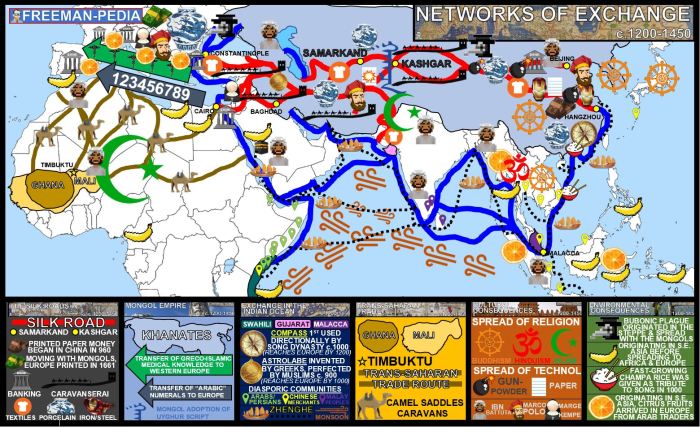
The spread of citrus fruits throughout the Mediterranean region occurred gradually over centuries. It was influenced by factors such as trade networks, military conquests, and cultural exchange.
Chronological Account of Citrus Spread
- 8th-9th centuries: Arab traders introduced citrus fruits to Spain and North Africa.
- 10th-12th centuries: The Crusades further facilitated the spread of citrus to Western Europe.
- 15th-16th centuries: European explorers brought citrus fruits to the Americas and other parts of the world.
Major Trading Networks and Empires
- Arab Empire: Arab traders played a pivotal role in the spread of citrus throughout the Mediterranean, establishing trade routes that connected the Middle East, North Africa, and Southern Europe.
- Venetian Empire: Venetian merchants played a significant role in the citrus trade, transporting citrus fruits from the Middle East to other parts of Europe.
- Spanish Empire: The Spanish conquistadors introduced citrus fruits to the Americas, where they quickly became a staple crop.
Role of Warfare and Conquest
- Arab Conquests: Arab conquests in the 7th and 8th centuries brought citrus cultivation to North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula.
- Crusades: The Crusades facilitated the exchange of agricultural knowledge and the spread of citrus cultivation to Western Europe.
Citrus Cultivation and Agriculture
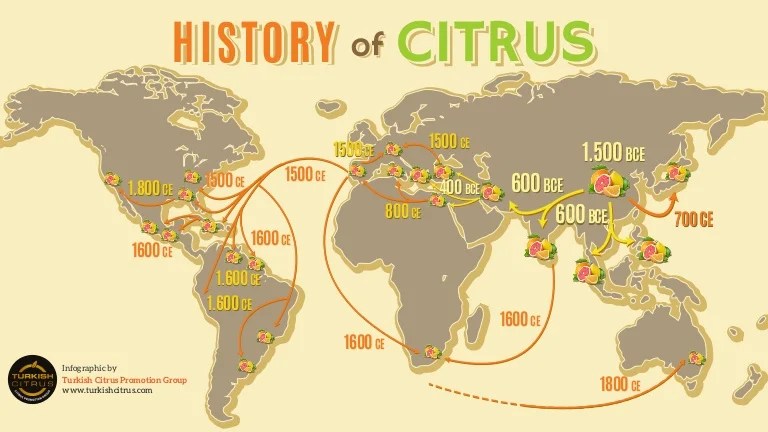
The cultivation of citrus fruits in the Mediterranean region requires specific environmental conditions and agricultural practices.
Cultivation Techniques, Spread of citrus in the mediterranean ap world history
- Grafting: Citrus trees are often grafted onto rootstocks to improve disease resistance, vigor, and fruit quality.
- Pruning: Pruning is essential for controlling tree size, promoting fruit production, and maintaining tree health.
- Irrigation: Citrus trees require regular irrigation, especially during the hot, dry summer months.
Environmental Conditions
- Climate: Citrus fruits thrive in warm, subtropical climates with mild winters and hot, dry summers.
- Soil: Well-drained, loamy soils with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 are ideal for citrus cultivation.
- Sunlight: Citrus trees require full sun exposure to produce abundant fruit.
Impact on Local Environment and Economy
- Deforestation: Citrus cultivation can lead to deforestation, as land is cleared for new orchards.
- Water consumption: Citrus trees require a significant amount of water, which can strain local water resources.
- Economic benefits: Citrus cultivation provides employment opportunities and generates revenue for local communities.
Economic and Social Impact of Citrus
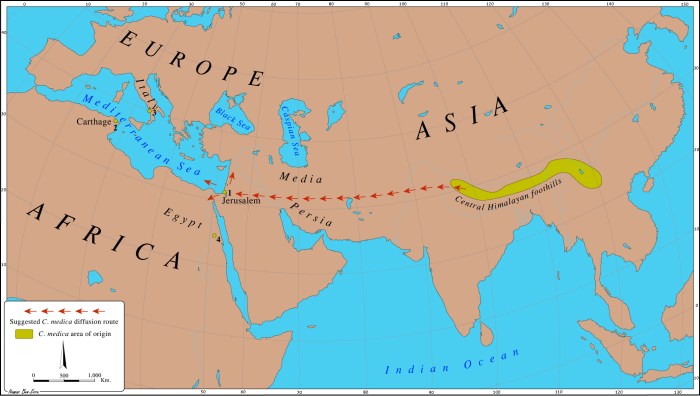
The spread of citrus in the Mediterranean had a profound economic and social impact on the region.
Economic Benefits and Opportunities
- Trade: Citrus fruits became a valuable commodity, traded throughout the Mediterranean and beyond.
- Agriculture: Citrus cultivation created new agricultural jobs and stimulated the development of supporting industries.
- Tourism: Citrus groves and orchards became popular tourist destinations.
Social and Cultural Significance
- Culinary: Citrus fruits became an essential ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine, used in both sweet and savory dishes.
- Medicine: Citrus fruits were used for medicinal purposes, particularly for their high vitamin C content.
- Symbolism: Citrus fruits became symbols of prosperity, abundance, and hospitality.
Environmental and Ecological Effects
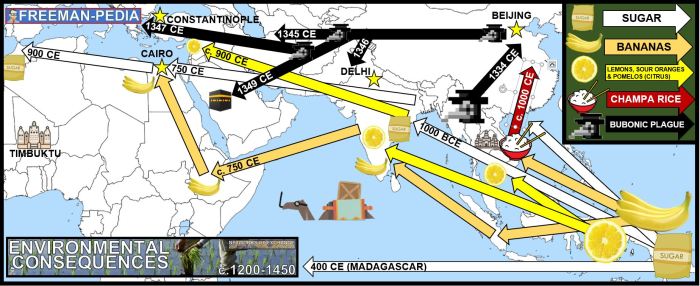
Citrus cultivation can have both positive and negative environmental and ecological effects.
Environmental Impacts
- Deforestation: Citrus cultivation can lead to deforestation, as land is cleared for new orchards.
- Water consumption: Citrus trees require a significant amount of water, which can strain local water resources.
- Pesticide use: Citrus cultivation can involve the use of pesticides, which can have negative impacts on the environment and human health.
Ecological Role
- Biodiversity: Citrus groves can provide habitat for a variety of wildlife.
- Ecosystem services: Citrus trees can help to regulate water flow and soil erosion.
Mitigation Measures
- Sustainable farming practices: Implementing sustainable farming practices, such as integrated pest management, can reduce the environmental impact of citrus cultivation.
- Water conservation: Using efficient irrigation systems and drought-tolerant citrus varieties can help to conserve water resources.
- Reforestation: Planting trees in areas where citrus orchards have been cleared can help to restore lost habitat and mitigate deforestation.
FAQ Resource
When were citrus fruits first introduced to the Mediterranean region?
Citrus fruits were first introduced to the Mediterranean region during the 10th century through trade with Arab merchants.
How did citrus cultivation impact the Mediterranean economy?
Citrus cultivation became a major source of income for many Mediterranean countries, as citrus fruits were highly valued for their nutritional value and medicinal properties.
What were some of the environmental effects of citrus cultivation in the Mediterranean?
Citrus cultivation led to deforestation and water depletion in some areas of the Mediterranean region, as large tracts of land were cleared for citrus groves.