Crash course astronomy #8 tides – Crash Course Astronomy #8: Tides sets sail on an adventure to explore the captivating interplay between the celestial bodies and our oceans. Embark on a voyage where we unravel the mysteries of how the Moon and Sun orchestrate the rhythmic rise and fall of the tides, shaping our planet’s coastal landscapes and influencing life within.
Delving into the gravitational embrace between the Moon and Earth, we’ll witness how the Moon’s gravitational pull tugs at our planet’s oceans, creating the familiar high and low tides. We’ll also uncover the Sun’s subtle yet significant contribution to the tidal symphony, revealing the intricate dance between these celestial giants.
Tides and the Sun
The Sun also exerts a gravitational pull on Earth, creating tides. However, the Sun’s tidal force is much weaker than the Moon’s.
The Sun’s Gravitational Pull
The Sun’s gravitational pull is about 170 times stronger than the Moon’s. However, the Sun is also much farther away from Earth than the Moon. This means that the Sun’s tidal force is about 2.2 times weaker than the Moon’s.
The Sun’s Tidal Force
The Sun’s tidal force creates two bulges on Earth’s surface: one on the side of Earth facing the Sun, and one on the opposite side of Earth.
The bulge on the side of Earth facing the Sun is caused by the Sun’s gravity pulling Earth’s water towards it. The bulge on the opposite side of Earth is caused by the Sun’s gravity pulling Earth’s center of mass away from the water.
The Sun’s tidal force is not strong enough to cause high and low tides. However, it does contribute to the tides, making them slightly higher during the day than at night.
Spring Tides and Neap Tides

The Moon’s gravitational pull is the primary cause of tides on Earth. However, the Sun also exerts a gravitational force on our planet, which influences the tides to a lesser extent. The combined gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun create two distinct types of tides: spring tides and neap tides.
Spring Tides
Spring tides occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun align, either on the same side (new moon) or opposite sides (full moon) of Earth. During these times, the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun reinforce each other, resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides.
The difference between high and low tides is at its maximum during spring tides.
Neap Tides
Neap tides occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun are perpendicular to each other. This happens during the first and third quarters of the Moon’s orbit around Earth. During neap tides, the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun partially cancel each other out, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides.
Crash Course Astronomy #8 Tides is an insightful episode that delves into the fascinating phenomenon of tides. The video explains how the gravitational pull of the moon and sun influences the rise and fall of Earth’s oceans. In a similar vein , Jeff uses 3 fifth-size strips to demonstrate the concept of ratios in mathematics.
Both topics illustrate the fundamental principles of celestial mechanics and numerical relationships, making them compelling viewing for anyone curious about the wonders of science.
The difference between high and low tides is at its minimum during neap tides.Spring tides typically occur around the time of new and full moons, while neap tides occur around the time of first and third quarter moons. These patterns can vary slightly depending on the specific location and the time of year.
Tidal Patterns

Tidal patterns vary significantly around the world, influenced by factors such as the shape of the coastline, the depth of the water, and the presence of underwater features like reefs and seamounts.
Some areas experience predictable, semi-diurnal tides, with two high tides and two low tides each day. Others exhibit mixed semi-diurnal tides, with two unequal high tides and two unequal low tides daily. Diurnal tides, with one high tide and one low tide per day, are also observed in some locations.
Coastal Shape and Tidal Patterns
The shape of the coastline can significantly impact tidal patterns. In bays and estuaries, the funnel-like shape amplifies the tidal range, leading to higher high tides and lower low tides. Conversely, headlands and peninsulas can reduce the tidal range.
Water Depth and Tidal Patterns, Crash course astronomy #8 tides
The depth of the water also influences tidal patterns. In shallow waters, tidal currents are more significant, resulting in stronger tides. In deeper waters, tidal currents are weaker, leading to smaller tidal ranges.
Examples of Tidal Patterns
- The Bay of Fundy in Canada experiences the highest tides in the world, with a tidal range of over 16 meters (52 feet).
- The Mediterranean Sea has mixed semi-diurnal tides, with a tidal range of about 0.5 meters (1.6 feet).
- The Gulf of Mexico exhibits diurnal tides, with a tidal range of less than 1 meter (3 feet).
Tidal Energy: Crash Course Astronomy #8 Tides

Tidal energy harnesses the power of the ocean’s tides to generate electricity. Tides occur due to the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on Earth’s oceans, resulting in the rise and fall of sea levels.
To capture this energy, various technologies have been developed, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Tidal Barrages
Tidal barrages are dams constructed across estuaries or tidal rivers. As the tide rises and falls, water flows through turbines in the barrage, generating electricity.
- Advantages:Predictable energy source, large-scale power generation.
- Disadvantages:High construction costs, environmental impacts on marine ecosystems.
Tidal Turbines
Tidal turbines are underwater turbines placed in areas with strong tidal currents. They operate similarly to wind turbines, with blades that rotate in the flowing water, generating electricity.
- Advantages:Lower environmental impact than barrages, can be deployed in various locations.
- Disadvantages:Less predictable energy output, smaller power generation capacity.
Tidal Lagoons
Tidal lagoons are enclosed areas of water created by constructing a barrier across a bay or estuary. Water flows in and out of the lagoon through turbines, generating electricity.
- Advantages:Can be built in areas with limited tidal range, reduced environmental impact compared to barrages.
- Disadvantages:Higher construction costs, potential for sedimentation issues.
Expert Answers
What causes tides?
Tides are primarily caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun on Earth’s oceans.
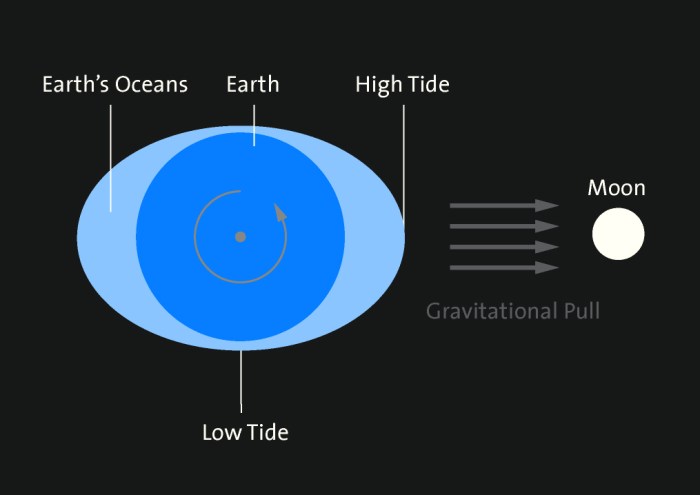
Why are there two high tides and two low tides each day?
The Earth rotates on its axis once a day, passing through the two high tides and two low tides created by the Moon’s gravity.
What are spring tides and neap tides?
Spring tides occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun align, resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides. Neap tides occur when the gravitational forces are at right angles, leading to less pronounced tides.